Synthesis of carbon nanostructures in arc with graphite electrodes
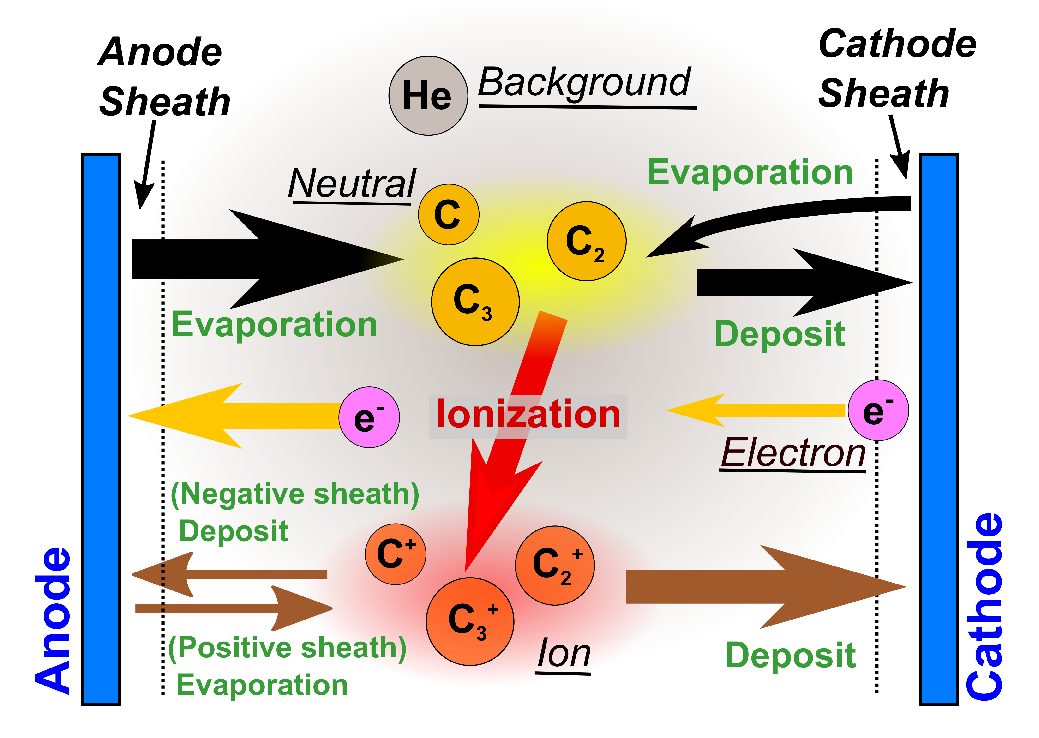
Figure 1: Schematic of atmospheric pressure arc plasma using graphite electrodes
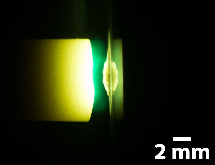
Figure 2: Photograph of the arc with graphite electrodes during operation
|
Laboratory for Plasma Nanosynthesis & Nanofabrication Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory |

|
Synthesis of carbon nanostructures in arc with graphite electrodes
We utilize an inert gas (e.g., helium or argon) DC arc discharge with a vaporized anode at atmospheric pressure, or anodic arc, which has been successfully applied to the synthesis of a broad class of nanomaterials, including carbon nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, and other nanostructures. Figure 1 shows the schematic of an atmospheric pressure arc plasma.

Figure 1: Schematic of atmospheric pressure arc plasma using graphite electrodes
Carbon neutral atoms evaporate from the anode, which is heated by plasma electrons. The ions created by ionization will then deposit to the cathode.

Figure 2: Photograph of the arc with graphite electrodes during operation

Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory managed by Princeton University.

Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory
P.O. Box 451
Princeton, NJ 08543-0451
GPS: 100 Stellarator Road
Princeton, NJ, 08540
(609) 243-2000
© 2025 Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. All rights reserved.